Understanding Leptospirosis in Cattle: Management, Control and Treatment
Leptospirosis in Cattle: Leptospirosis is a zoonosis that affects various animals, including cattle, and represents a significant challenge for livestock farming. Understanding the transmission mechanisms, symptoms and management strategies is essential for controlling and preventing this disease, which can cause major economic and health losses.
In this article, we will explore in detail how leptospirosis manifests itself in cattle, what the effective methods of control and treatment are, and how adopting good practices can minimize the risks of infection.
What is Leptospirosis?
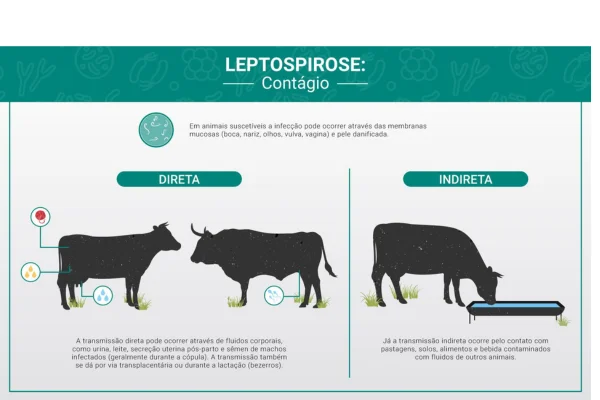
Leptospirosis is caused by the bacterium LeptospiraThe disease is mainly transmitted through the urine of infected animals and can contaminate water and soil. Infection in cattle occurs when these animals come into contact with contaminated environments, such as ponds, puddles and flooded pastures. The disease is more common in regions with high rainfall, where environmental factors favor the survival of leptospires.
Contents
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in Cattle
The symptoms of leptospirosis in cattle can vary significantly, from asymptomatic forms to serious conditions that lead to death. The most common clinical signs include fever, apathy, loss of appetite, jaundice (yellowing of the mucous membranes), hemoglobinuria (presence of blood in the urine) and abortions. In more severe cases, the animals may present renal and hepatic failure, making early diagnosis essential for successful management of the disease.
To confirm the presence of Leptospiralaboratory tests are carried out, such as serology, which detects the presence of specific antibodies against the bacteria, and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), which identifies the DNA of the bacterium. Leptospira in the animals' blood or urine. The combination of these tests increases the accuracy of the diagnosis, allowing for more effective treatment and the implementation of appropriate control measures.
Management and Prevention: Strategies to Control Leptospirosis
Hygiene and Environmental Control
Cleaning and disinfecting grazing areas, drinking fountains and resting places are essential measures to reduce the load of Leptospira in the environment. Draining flooded areas and using chemical products such as sodium hypochlorite can help eliminate the bacteria present in the water and soil. In addition, building fences and dividing grazing areas helps to prevent cattle from coming into direct contact with possible sources of infection.
Vaccinating cattle
Vaccination is one of the most effective strategies for preventing leptospirosis. There are different vaccines available on the market, which protect animals against the main strains of Leptospira. Vaccination should be carried out according to the protocol recommended by the veterinarian, usually involving two initial doses with an interval of 21 to 30 days, followed by annual boosters. As well as protecting the animals, vaccination helps to reduce the spread of the bacteria on the property.
Herd Monitoring and Control
Continuous monitoring of the herd is essential to identify cases of leptospirosis early on. This includes carrying out periodic serological tests and closely observing animals for clinical signs of the disease. Isolating suspected animals and treating them immediately with appropriate antibiotics helps to control the spread of the disease and minimize economic impacts.
Treatment of Leptospirosis: The Role of Antibiotics
The treatment of leptospirosis in cattle involves the administration of antibiotics, which should be chosen on the basis of the sensitivity of the bacteria. Leptospira isolated in laboratory tests. The most commonly used antibiotics include penicillin and macrolides, which are effective against the bacteria. It is crucial to follow the veterinarian's advice on the dosage and duration of treatment, as complete eradication of the bacterium is essential. Leptospira depends on adequate and prolonged treatment.
In addition to antibiotics, it is important to provide support to affected animals, ensuring good nutrition and hydration, and treating complications such as kidney or liver failure. The administration of electrolyte solutions and intravenous fluids may be necessary to maintain the animals' health during treatment.
Economic Impacts of Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis not only affects the health of the animals, but also has significant economic implications for producers. Losses can occur in a variety of ways, including reduced milk production, increased calf mortality, costs for medical treatment and control measures, as well as the loss of value of infected animals. Therefore, investing in preventative measures is an essential strategy for mitigating these impacts and ensuring the sustainability of livestock production.
Good Livestock Practices: Preventing Leptospirosis
Adopting good herd management practices is key to preventing leptospirosis and other diseases. This includes:
- Keep animals in clean, dry areasavoiding waterlogged pastures.
- Carry out annual vaccinationsaccording to the recommended timetable.
- Isolating suspicious animals of leptospirosis and start immediate treatment.
- Implement rodent control programs and other wild animals, which can be reservoirs of the bacteria.
- Educating and training farm staff about the clinical signs of the disease and preventive measures.
The Importance of Education and Training
Educating farmers and farm workers about the risks of leptospirosis and best management practices is crucial to the success of prevention and control strategies. Disseminating information through workshops, courses and educational materials can enable those involved in livestock farming to recognize the signs of the disease and take quick and effective action to prevent outbreaks.
Conclusion: The road to sustainable livestock farming
Leptospirosis represents a constant challenge for livestock farmers, but with the right knowledge and the implementation of effective management and control measures, it is possible to significantly reduce the risks of infection and guarantee the health of the animals. The combination of environmental management practices, vaccination, constant monitoring and appropriate treatment is essential for controlling the disease.
Investing in technology, training and good management practices not only protects cattle from leptospirosis, but also contributes to the sustainability and profitability of production. With an integrated approach and an ongoing commitment to animal health, farmers can meet the challenges of leptospirosis and build a safer and more productive livestock sector.
References
- World Organization for Animal Health (OIE)
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Supply (MAPA)
With this complete overview, we hope to have clarified the main doubts about leptospirosis in cattle and offered practical guidelines for managing and controlling the disease. If you are a cattle farmer or work in the area, keep up to date and don't hesitate to seek professional advice to ensure the health and well-being of your animals.