How long does a shark live?
The Life of Sharks
How Long a Shark Lives and Factors that Influence its Longevity
How Long Does a Shark Live - Sharks, with their imposing shapes and fundamental roles in marine ecosystems, have always fascinated scientists and lovers of marine life. One of the questions that often arises is: how long does a shark live? To answer this question, we need to explore the different species of sharks, understand the factors that affect their longevity and consider the threats they face in the ocean. In this article, we will dissect these aspects and provide a comprehensive insight into the lives of these magnificent predators.
The Life Expectancy of Sharks
The life expectancy of sharks varies significantly between different species. Some sharks live only a few years, while others can reach impressive ages. Here are some examples:
Contents
- White shark (Carcharodon carcharias)One of the best-known sharks, the great white can live for between 30 and 70 years, depending on factors such as its diet and environment.
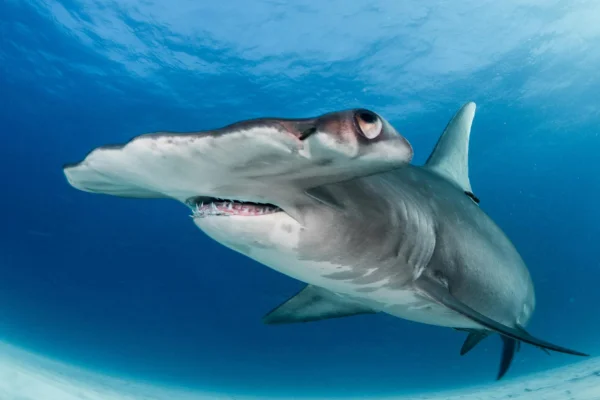
- Hammerhead shark (Sphyrna spp.)Species such as the common hammerhead shark can live between 20 and 30 years, although some individuals can live longer in ideal conditions.
- Blacktip shark (Carcharhinus spp.)These sharks have a shorter life expectancy, ranging from 10 to 20 years.
These variations are influenced by a combination of biological and environmental factors.

Factors Influencing the Longevity of Sharks
1. Species
The species is the most direct factor affecting the longevity of sharks. Smaller species generally have a shorter lifespan, while larger ones can live for several decades. Differences in life expectancy between species can be attributed to evolutionary adaptations and their role in the marine ecosystem.
2. Size and Growth
The size of a shark is often related to its longevity. Larger sharks, such as the great white, tend to live longer than smaller species. This may be related to the fact that larger sharks have fewer natural predators and less competition for resources.
3. Growth Rate
Growth rate also influences longevity. Sharks that grow quickly may reach sexual maturity earlier, but this doesn't always mean that they will live longer. Slow-growing species, such as the Greenland shark, can take decades to reach maturity and consequently live longer.
4. Environment and Living Conditions
The marine environment in which a shark lives can have a significant impact on its longevity. Sharks that live in protected areas with an abundance of food tend to live longer. On the other hand, sharks in regions with high pollution or a shortage of resources can face challenges that reduce their life expectancy.
5. Predators and Threats
Sharks, despite being top predators, still face natural and human threats. Natural predators, such as orcas and large sharks, can affect the longevity of smaller sharks. In addition, commercial fishing and habitat destruction are significant threats that impact shark life.
Sharks and Their Adaptations for Long Life
Some sharks have special characteristics that allow them to live longer than others. The Greenland shark is a notable example. Studies indicate that this shark can live up to 400 years, making it one of the longest-lived vertebrates on the planet. This longevity can be attributed to its extremely slow metabolism and the icy environment in which it lives.
Another example is the whale shark, the largest fish in the ocean. This giant can live between 70 and 100 years. Its long life may be related to its role as a filter-feeder, which reduces the amount of direct competition for food.
The Impact of Human Activity on Shark Longevity
Human activity has a profound impact on the lives of sharks. Commercial fishing is one of the biggest threats they face. Many shark species are hunted for their fins, meat and oil, leading to a sharp decline in their populations. In addition, pollution and destruction of the marine habitat affect the quality of the environment in which sharks live, reducing their longevity.
1. Commercial Fishing
Commercial fishing, including finning and bycatch, is a significant threat to many sharks. Accidental capture in fishing nets, known as bycatch, often results in the death of sharks that become trapped unintentionally.
2. Marine pollution
Ocean pollution, including plastics and toxic chemicals, can damage the health of sharks and affect their environment. These pollutants can compromise water quality and available food resources, impacting sharks' longevity.
3. Habitat destruction
The destruction of marine habitats, such as coral reefs and feeding areas, also affects the lives of sharks. The loss of these critical environments can reduce the availability of food and safe places for sharks, decreasing their life expectancy.

The Importance of Shark Conservation
Shark conservation is crucial to maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. As top predators, sharks play a vital role in controlling the populations of other species and maintaining the health of the oceans. Preserving these species not only helps to protect marine biodiversity, but also ensures the continuity of ecological processes that benefit the entire marine environment.
1. Conservation measures
Various conservation measures are underway to protect sharks. These include the creation of marine protected areas, fishing regulations and public awareness campaigns. Conservation organizations are working to reduce incidental catches and promote sustainable fishing practices.
2. Education and Awareness
Education and awareness about the importance of sharks are essential to promote their conservation. Educational programs and awareness campaigns help inform the public about the role of sharks in the marine ecosystem and the need to protect them.
3. Research and Monitoring
Ongoing research into shark species and their habitats is essential to better understand their needs and threats. Monitoring shark populations helps to identify trends and assess the effectiveness of conservation measures.
Conclusion - How Long Does a Shark Live?
The question of how long does a shark live? reveals a fascinating complexity. The longevity of sharks is influenced by a variety of factors, including the species, the environment and the threats they face. While some species can live for just a decade, others can reach impressive ages of up to 400 years. Understanding these aspects is essential for the conservation and protection of these incredible creatures. Protecting sharks not only helps preserve a vital part of the oceans, but also ensures the health and sustainability of marine ecosystems as a whole.