Are raccoons dangerous or do they transmit diseases?
Introduction:
Raccoons, known for their striking appearance and adaptable behavior, are animals that arouse curiosity and discussion about their coexistence with humans. These charming mammals, often found in varied habitats, raise questions about the possible dangers associated with their presence and the transmission of diseases. In this article we will explore the characteristics of raccoons, their behavior, as well as considerations about the risks they may pose to public health.
Raccoons: Learn More About Them
Raccoons are mammals known for their captivating appearance and curious behavior. Found mainly in North and Central America, these animals have aroused interest and, in certain cases, raised concerns about possible dangers associated with their presence near humans, as well as the transmission of diseases.
Contents
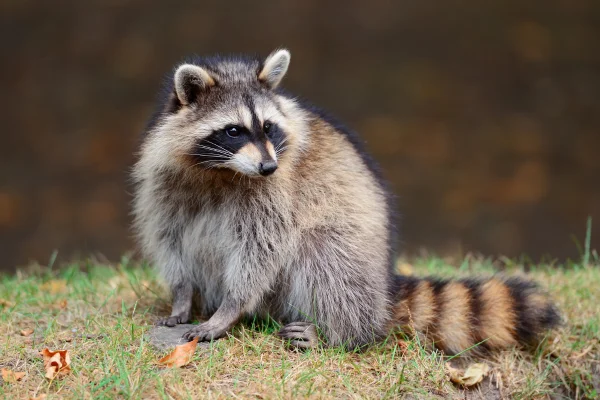

Raccoon characteristics
Raccoons, scientifically known as Procyon lotorThey are recognizable by their light grey to brown coat, adorned with black stripes around the eyes, which gives them a distinctive appearance. They are medium-sized animals with agile bodies and striped tails.
With adaptive abilities, raccoons show remarkable intelligence, using their agile forepaws to manipulate objects and explore environments. They are mainly crepuscular and nocturnal animals, foraging at night and resting during the day.
Raccoon Behavior and Habitat
These mammals are known for their adaptability to a variety of environments, from forests to urban areas. Raccoons are omnivores and their diet covers a wide range of foods, including fruit, insects, eggs, small mammals and even human waste when available, which often brings them closer to areas inhabited by people.
In addition to their prowess in searching for food, raccoons build burrows or use cavities in trees for shelter, showing territorial behavior at certain times of the year, especially during mating season.
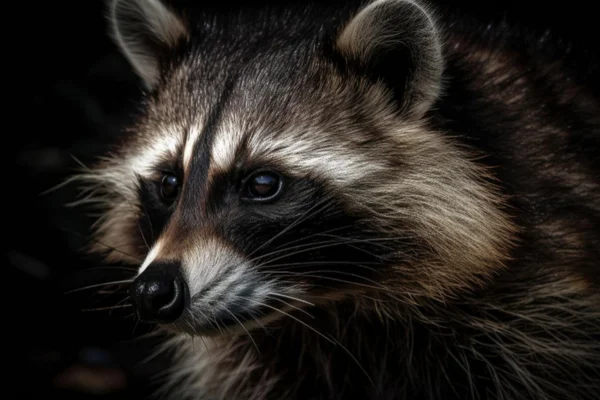

Dangers and Diseases on The raccoon
One of the concerns associated with raccoons is the possible transmission of diseases to humans and other animals. These animals can be carriers of various pathogens, including the rabies virus, leptospirosis and bacteria such as Baylisascaris procyonisan intestinal parasite.
Although the transmission of diseases by raccoons is a concern, it is important to note that the risk is relatively low and can be mitigated through simple measures, such as avoiding direct contact with these animals, keeping vaccinations up to date for pets and not feeding raccoons, avoiding attracting these animals to residential areas.
Coexistence and Risk Mitigation
To minimize unwanted encounters with raccoons and potential health risks, some measures can be adopted:
- Keep outdoor areas clean, without easy access to food or garbage.
- Close garbage cans securely and use animal-proof containers.
- Seal openings in buildings and constructions that could serve as shelter for these animals.
- Avoid feeding raccoons or any other form of wildlife.
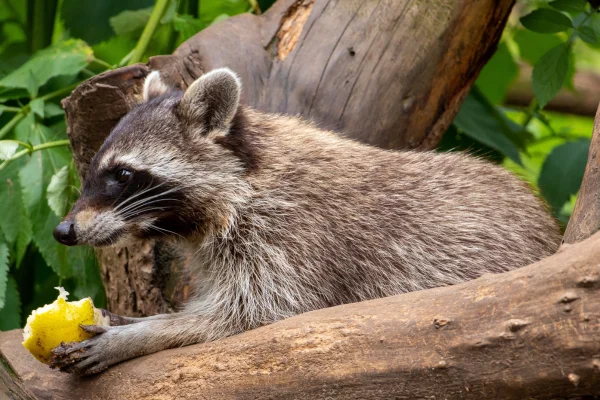

Conclusion: The raccoon
Raccoons are fascinating animals that play a vital role in the ecosystems they inhabit. Although they may pose minimal risks of disease transmission, harmonious coexistence with these mammals can be achieved by understanding their characteristics and behaviour, along with implementing practices that minimize possible encounters and risks to public health.
Therefore, when encountering raccoons or any other wildlife, it is essential to respect their nature and act responsibly, maintaining harmony between the human environment and the animal world.
Frequently Asked Questions about Raccoons:
1. Are raccoons dangerous to humans?
Although raccoons are not naturally aggressive, their close interaction with humans can pose risks. It is important to keep your distance and not try to approach or feed these animals.
2. Do raccoons transmit diseases?
Yes, raccoons can carry diseases such as rabies, leptospirosis and intestinal parasites. However, the risk of transmission is low and can be mitigated through preventative measures.
3. How can I avoid unwanted encounters with raccoons?
Keeping outdoor areas clean, closing garbage cans securely and sealing openings in buildings are all effective measures to prevent these animals from being attracted to residential areas.
4. What should I do if I find an injured or sick raccoon?
Avoid direct contact with the animal and contact local authorities or wildlife experts to deal with the situation. Do not attempt to rescue or deal with injured raccoons on your own.
5. Are raccoons protected by environmental laws?
In many regions, raccoons are protected by environmental laws that regulate their capture, transportation and handling. Check your local regulations for specific information on the protection of these animals.
6. What role do raccoons play in ecosystems?
Raccoons play an important role in controlling populations of insects and small mammals, helping to maintain balance in the ecosystems they inhabit.
7. Can I keep a raccoon as a pet?
In many areas, keeping a raccoon as a pet is illegal due to regulations and also because they are wild animals that require specialized care and a suitable environment to live healthily.
Thanks for stopping by, check out our other work too
https://vettopbr.com/tosse-em-caes/