Baylisascaris procyonis infection
The Hidden Danger of Raccoon Roundworm
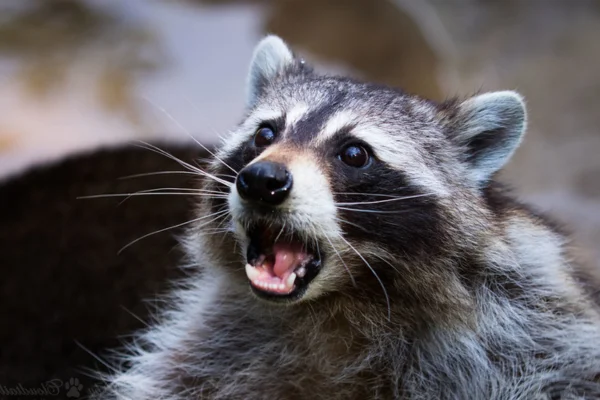
Raccoons are fascinating creatures, often admired for their peculiar appearance and cunning behavior. However, these charismatic animals can carry a dangerous parasite that poses a significant threat to other animals and humans: raccoon roundworm, scientifically known as Baylisascaris procyonis.
Although it is a relatively unknown infection, raccoon roundworm infection can have serious consequences and has become a public health concern in several regions.
What is Baylisascaris procyonis?
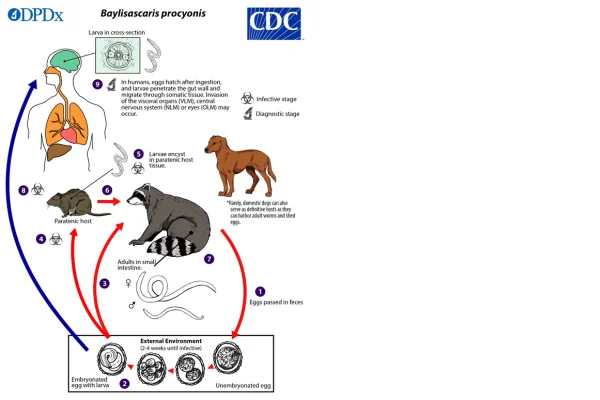
A Baylisascaris procyonis is a parasitic roundworm that resides in the intestines of raccoons. Raccoons are the natural hosts of this parasite, which normally causes no health problems for them. However, when other animals or humans accidentally ingest the parasite's microscopic eggs, the results can be devastating.
Contents
Roundworm eggs are eliminated in raccoon feces and can remain viable in the environment for years. They are resistant and can survive in soil, on surfaces or even in water, becoming a source of infection for any organism that comes into contact with them.
How does infection occur?
Infection with Baylisascaris procyonis occurs mainly through the accidental ingestion of eggs present in contaminated soil, water or on surfaces that have been exposed to raccoon feces. Young children, who tend to put objects in their mouths, are particularly at risk, as are people who work or spend time in areas where raccoons are common.
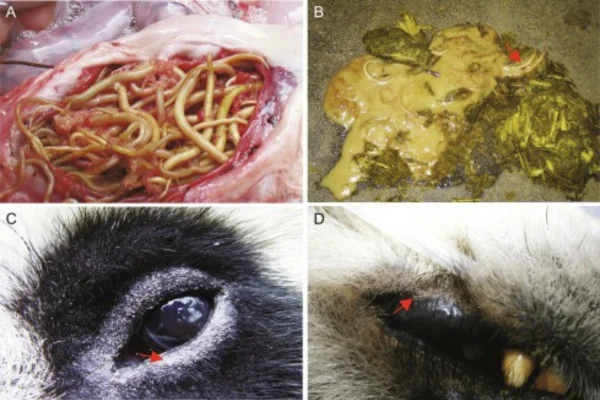
The eggs, once ingested, hatch in the small intestine, releasing larvae that can migrate to different parts of the body. This migration can cause significant damage, depending on the organs affected, including the brain, eyes, liver and lungs. This process is known as "larva migrans" and can lead to serious complications such as encephalitis, loss of vision and even death in more extreme cases.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The symptoms of raccoon roundworm infection can vary widely, depending on where the larvae have migrated and the intensity of the infection. Initially, symptoms can be non-specific, such as nausea, fatigue, loss of appetite and abdominal pain. However, as the larvae move to other tissues, more serious symptoms can include:
- Neurological: intense headaches, convulsions, loss of coordination, muscle weakness and, in severe cases, coma.
- Eyepieces: blurred vision, eye pain, inflammation of the eye, and in severe cases, blindness.
- Respiratory: difficulty breathing, coughing and inflammation of the lungs.
The diagnosis of Baylisascaris procyonis is challenging, especially since the symptoms can mimic several other conditions. A history of exposure to areas where raccoons are common, combined with specific clinical symptoms, can raise suspicions. Laboratory tests, such as stool tests or serology, can help confirm the presence of antibodies against the parasite, although a definitive diagnosis is often made after the larvae have been identified in the affected tissues, which can occur post-mortem.
Treatment and prognosis
Unfortunately, there is no specific treatment for the Baylisascaris procyonis that is universally effective. However, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to minimizing damage. Anti-parasitic drugs, such as albendazole, can be administered to try to kill the larvae before they migrate to vital organs. In cases where the central nervous system or eyes are already affected, treatment may involve corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and other supportive therapies.
The prognosis for patients infected with Baylisascaris procyonis varies depending on the severity and extent of the infection. Mild cases can resolve with appropriate treatment, but more serious infections can result in permanent damage or death.
Prevention: The best defense
Given the devastating potential of raccoon roundworm infection, prevention is essential. Some preventative measures include:
- Avoid contact with raccoons and their droppings: This is especially important in areas where raccoons are common. Do not feed raccoons and discourage their presence near homes by sealing garbage cans and removing outdoor food sources.
- Education and awareness: Teach children about the dangers of playing in areas that may be contaminated with raccoon droppings. Supervise them in parks and outdoor areas.
- Personal hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly after any outdoor activity and before eating, especially if you have been in areas where raccoons have been seen.
- Keep outdoor areas clean: Remove raccoon feces immediately, using gloves and protective equipment to avoid direct exposure to the eggs.
- Raccoon control in urban areas: Implementing raccoon control measures in areas where contact with humans is frequent can help reduce the risk of infection.
Final considerations
Raccoon roundworm infection (Baylisascaris procyonis) is a serious disease that deserves attention due to its potential to cause significant damage to human and animal health. Although it is relatively rare, the effects can be devastating, making prevention and awareness essential. By avoiding contact with raccoons and their feces, maintaining proper hygiene practices and educating the public about the risks, it is possible to significantly reduce the chances of infection.
In addition, it is important that doctors and public health professionals are aware of this infection, especially in areas where raccoons are common, to ensure that diagnoses are made quickly and accurately. The management of Baylisascaris procyonis requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining prevention efforts, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment to protect both human and animal health.
Knowledge about Baylisascaris procyonis and measures to prevent its spread are essential to keep communities safe, especially in regions where contact with raccoons is frequent. Awareness is the first line of defense against this silent but dangerous infection.
Othank you for visiting us, check out our other work
https://vettopbr.com/cachorros/








